In the ever-evolving world of JavaScript programming, simply knowing how to write code is not enough. To truly build efficient, optimized, and scalable applications, you need to master two core concepts: Data Structures and Algorithms. These are not just dry academic knowledge—they are powerful tools that help you solve problems smartly and effectively.

This article will help you explore the fascinating world of data structures and algorithms, right in the familiar environment of JavaScript.
Why Should JavaScript Developers Care? 🤔
Many front-end developers or JavaScript beginners often ask: "Why do I need to learn these complex things?" The answer is simple:
- Performance optimization: Choosing the right data structure and algorithm can significantly reduce your app's runtime and memory usage. A smooth-running web app or a lightning-fast website is often the result of such optimizations.
- Effective problem solving: When facing a complex problem, instead of "guess-coding," you'll have a system of proven methods to analyze and find the optimal solution.
- Foundation for growth: This is fundamental knowledge in computer science. Mastering it makes it easier to learn new technologies, other programming languages, and understand how computers work at a deeper level.
- Ace technical interviews: Most technical interviews at top tech companies (Google, Facebook, Amazon, etc.) revolve around data structures and algorithms. This is how they assess a candidate's problem-solving mindset.
In short, it's a worthy investment for any developer who wants to go further in their career.
Common Data Structures in JavaScript
A data structure is a way of organizing, managing, and storing data so it can be accessed and modified efficiently. JavaScript, with its flexible nature, provides several built-in structures and allows us to easily build more complex ones.
1. Array
This is the most basic and widely used data structure. Arrays in JavaScript are extremely flexible, can hold different data types, and are dynamically sized.
- Strengths: Fast element access by index (
O(1)). - Weaknesses: Adding/removing elements at the start or in the middle can be slow (
O(n)) because other elements need to be shifted. - Use cases: Storing lists, foundation for many other data structures.
const fruits = ['Apple', 'Banana', 'Cherry']
console.log(fruits[1]) // Output: Banana (fast access)
fruits.unshift('Avocado') // Add to start (slower)
2. Object
While Arrays organize data in order, Objects organize data as key-value pairs. This is the foundation of almost everything in JavaScript.
- Strengths: Fast access, addition, and deletion by key.
- Use cases: Representing real-world entities (users, products), creating Hash Maps.
const user = {
id: 1,
name: 'John Doe',
email: 'john.doe@example.com',
}
console.log(user.name) // Output: John Doe
3. Set
A Set is a collection of unique values. Each value can only appear once in a Set.
- Strengths: Very fast existence checks. Efficiently removes duplicates.
- Use cases: Storing unique IDs, filtering unique values from an array.
const numbers = new Set([1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5])
console.log(numbers) // Output: Set(5) { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 }
console.log(numbers.has(3)) // Output: true
4. Map
Like Objects, Maps store data as key-value pairs. However, Maps have several advantages:
- Keys can be any data type (including objects, functions), while Object keys can only be strings or symbols.
- Maintains insertion order.
- Easy to get size (
.size). - Use cases: Storing metadata for objects, creating caches.
const userMap = new Map()
const user1 = { id: 1 }
userMap.set(user1, { name: 'Alice', role: 'Admin' })
console.log(userMap.get(user1)) // Output: { name: 'Alice', role: 'Admin' }
5. Custom Data Structures
Beyond built-in structures, understanding and building classic structures will level up your skills:
- Linked List: A chain of nodes linked together. Very efficient for adding/removing at the start (
O(1)). - Stack (LIFO): Last-In, First-Out. Like a stack of plates. Used for undo/redo, tree traversal.
- Queue (FIFO): First-In, First-Out. Like a line at the checkout. Used for async task management, BFS.
- Tree: Hierarchical structure with a root node and child nodes. Binary Search Tree is a common type, great for searching, adding, deleting data efficiently—average
O(log n). - Graph: Complex structure with vertices and edges. Used to model networks like social media, maps.
Essential Algorithms to Master
An algorithm is a set of steps or rules to solve a specific problem.
1. Sorting Algorithms
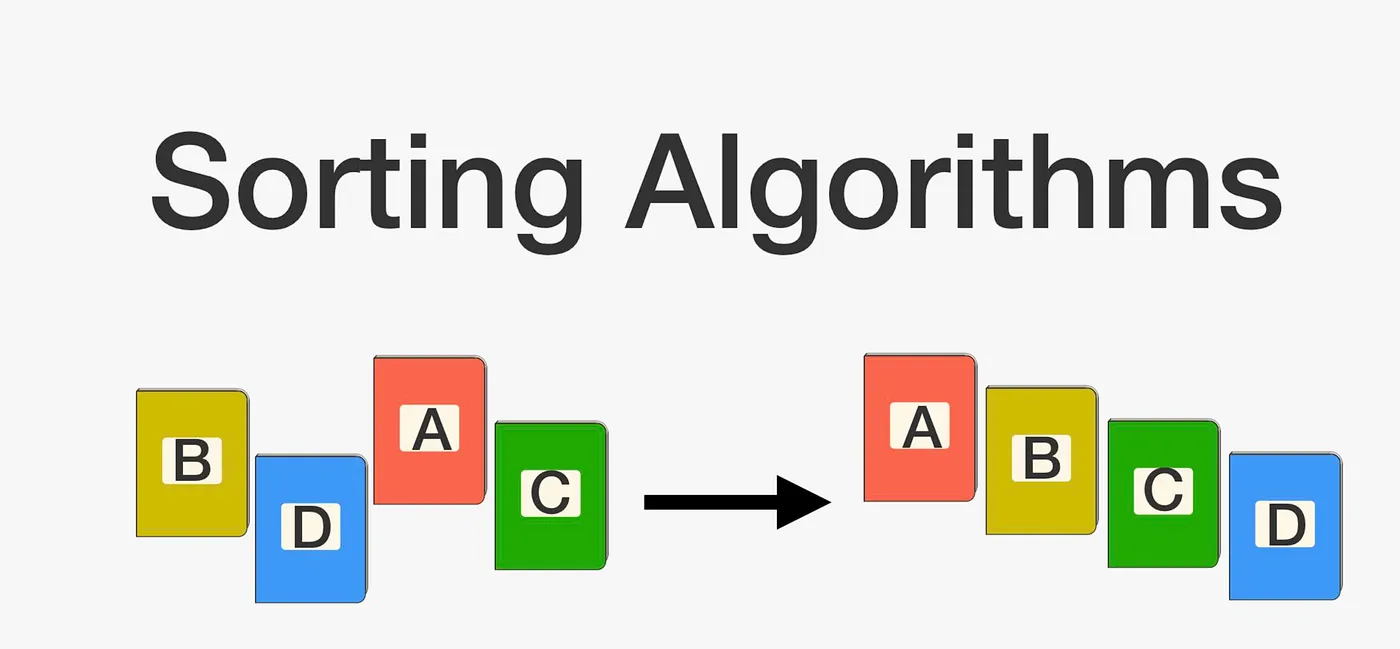
- Bubble Sort, Selection Sort, Insertion Sort: Simple, easy to understand, good for beginners but inefficient for large data (
O(n²)). - Merge Sort, Quick Sort: Much more efficient—average
O(n log n). These are commonly used in practice. JavaScript'sArray.prototype.sort()is often implemented with a variant of these.
2. Searching Algorithms

- Linear Search: Checks each element until found. Simple but slow (
O(n)). - Binary Search: Extremely efficient (
O(log n)), but requires sorted data. It works by repeatedly dividing the search space in half.
3. Recursion
A technique where a function calls itself. Recursion helps solve problems that can be broken down into similar subproblems (e.g., tree traversal, calculating factorial).
4. Tree and Graph Traversal Techniques
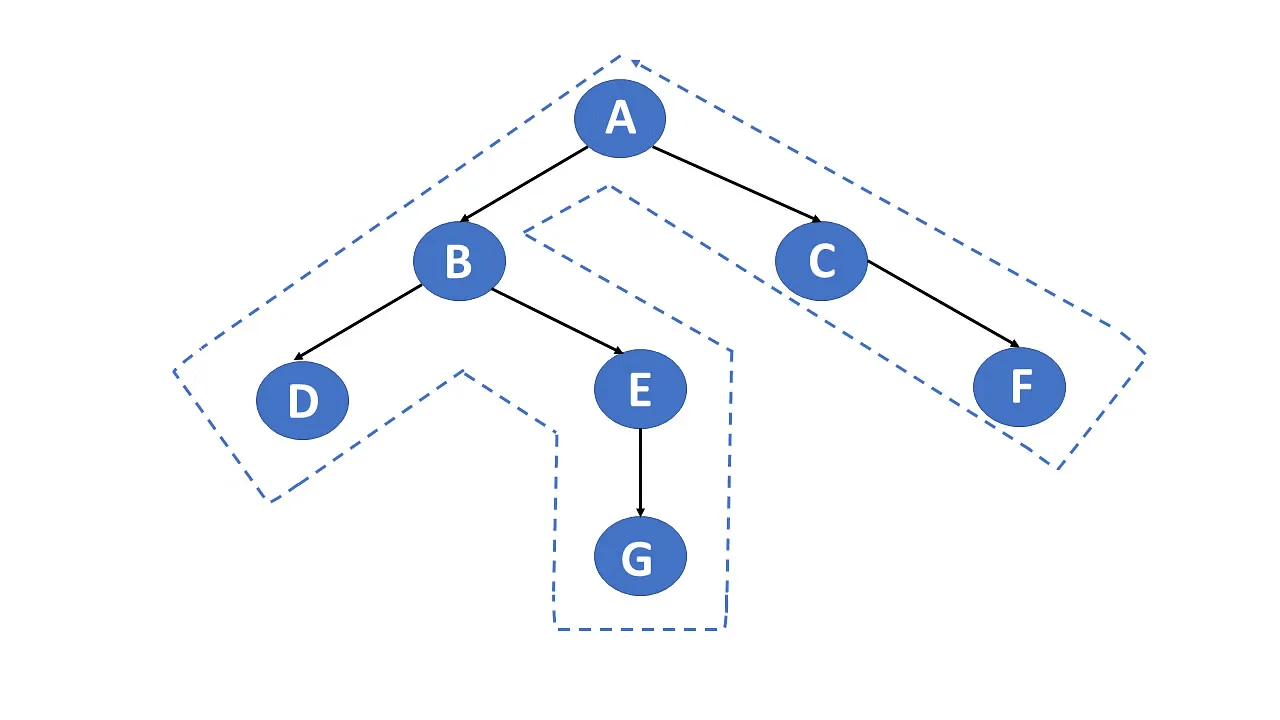
- Breadth-First Search (BFS): Visits nodes level by level. Uses a Queue.
- Depth-First Search (DFS): Goes deep into one branch before backtracking. Uses a Stack or recursion.
Learning Roadmap & Useful Resources 📚
Optimal learning roadmap:
- Master JavaScript basics: Make sure you understand
Array,Object,class,this, and async concepts. - Start with basic data structures: Learn and implement
Array,Linked List,Stack,Queue. - Move to more complex structures: Conquer
Tree(especially Binary Search Tree) andGraph. - Learn algorithms in parallel: Understand time and space complexity (
Big O Notation). Start with basic sorting and searching, then move to more advanced algorithms. - Practice relentlessly: This is the most important part.
Great practice platforms:
- LeetCode: The gold standard for interview prep and problem solving.
- HackerRank: User-friendly interface, lots of topic-based exercises.
- CodeSignal: Offers realistic interview simulation tests.
Conclusion: A Challenging Journey
The journey to mastering Data Structures and Algorithms with JavaScript can be challenging, but the rewards are well worth it. It not only helps you write better code but also sharpens your logic, analysis, and systematic problem-solving skills.
Start today, step by step, and you'll find yourself becoming a more well-rounded and professional JavaScript developer than ever before. Good luck on your journey!
![[Advanced JS] What is an IIFE? Advanced Applications of IIFE in JavaScript](/images/blog/iife-in-javascript.webp)
![[Advanced JS] What is a Closure? Advanced Applications of Closures in JavaScript](/images/blog/closures-in-javascript.webp)
![[Advanced JS] What is the Event Loop? Discover How JavaScript Works](/images/blog/event-loop-and-how-javascript-works.webp)
![[Advanced JS] Call, Apply, Bind in JavaScript: Clear Examples and Practical Applications](/images/blog/call-apply-bind-in-javascript.webp)