Have you ever wondered how a website can "remember" your shopping cart even after you shut down your computer, or how you stay logged in to Facebook for days without visiting? The magic behind these convenient experiences is the browser's data storage capabilities, and the three giants ruling this land are Cookies, LocalStorage, and SessionStorage.
They're not rivals, but tools with distinct missions. Understanding the nature, strengths, and weaknesses of each will help developers build smarter web apps and give users deeper insight into the web world. Let's explore them all in this article!
1. Cookies: The "Chatty" Old-Timer 🍪
Cookies are the oldest technology, dating back to the early days of the Internet. Think of a Cookie as a small "ticket" or "pass" that the server gives to your browser.
Every time your browser sends a request to that server (e.g., loading a new page, submitting a form), it attaches this "ticket." Based on the info on the ticket, the server can recognize who you are and what you did before.
Key features:
- Very small size: Only about 4KB. Just enough for basic identification info.
- Automatically sent: This is the "chatty" part. Whether you want it or not, all Cookie data is automatically attached to every HTTP request sent to the same domain. This can unnecessarily increase request size and affect performance.
- Expiration date: Cookies can be set to expire. If not, they're deleted when you close the browser.
- Two-way communication: Cookies can be created by both the server (server-side) and the browser (client-side).
When should you use Cookies?
- User authentication: Storing authentication tokens to maintain login state is the most common and effective use case.
- Tracking behavior: Analytics tools like Google Analytics use Cookies to track user behavior on the site.
- Basic personalization: Store simple preferences like your chosen language.
// Example: Create a Cookie that lasts for 7 days
document.cookie =
'username=Gemini; expires=Fri, 28 Sep 2025 12:00:00 UTC; path=/'
2. LocalStorage and SessionStorage: The Modern Duo 💾
To overcome the limitations of Cookies (small size, automatic sending), HTML5 introduced the Web Storage API, which includes LocalStorage and SessionStorage. Think of them as personal "storage lockers," spacious and only residing in your browser.
LocalStorage: The Durable Safe
Think of LocalStorage as a notebook that never gets lost or a personal safe in your browser. Data you store here will persist forever, across browser restarts and computer reboots, until you or the web app explicitly delete it.
Key features:
- Large capacity: About 5-10MB depending on the browser, much larger than Cookies.
- Client-side only: This data is never automatically sent to the server. It's only accessible via client-side JavaScript. This reduces server load and speeds up page loads.
- Never expires automatically: Data persists until deleted.
- Origin-scoped: Data is shared across all tabs and windows with the same origin (protocol, domain, and port).
When should you use LocalStorage?
- Store UI settings: For example, light/dark mode.
- Store non-sensitive user data: Unchecked shopping carts, draft content to prevent loss on reload.
- Store application state: Helps web apps load faster on reload.
// Store data
localStorage.setItem('theme', 'dark')
// Read data
let currentTheme = localStorage.getItem('theme') // 'dark'
// Remove data
localStorage.removeItem('theme')
SessionStorage: The Smart Scratchpad
If LocalStorage is a safe, SessionStorage is a scratchpad. It works just like LocalStorage, but with one key difference: data only exists for a single session.
A "session" here means a browser tab. When you close that tab, all SessionStorage data for that tab is wiped.
Key features:
- Large capacity: Similar to LocalStorage (about 5-10MB).
- Client-side only: Just like LocalStorage.
- Auto-cleared on tab close: This is the most important difference.
- Tab-scoped: Data in one tab's SessionStorage can't be accessed from another tab, even with the same origin.
When should you use SessionStorage?
- Store multi-step form data: For complex registration forms, you can store previous step data in SessionStorage. If the user reloads, the data isn't lost, but when they close the tab, the sensitive info is gone.
- Store temporary page state: For example, product filters selected by the user on an e-commerce page.
// Store data for the current session
sessionStorage.setItem('formData', '{"name": "John Doe"}')
// Read data
let savedForm = sessionStorage.getItem('formData')
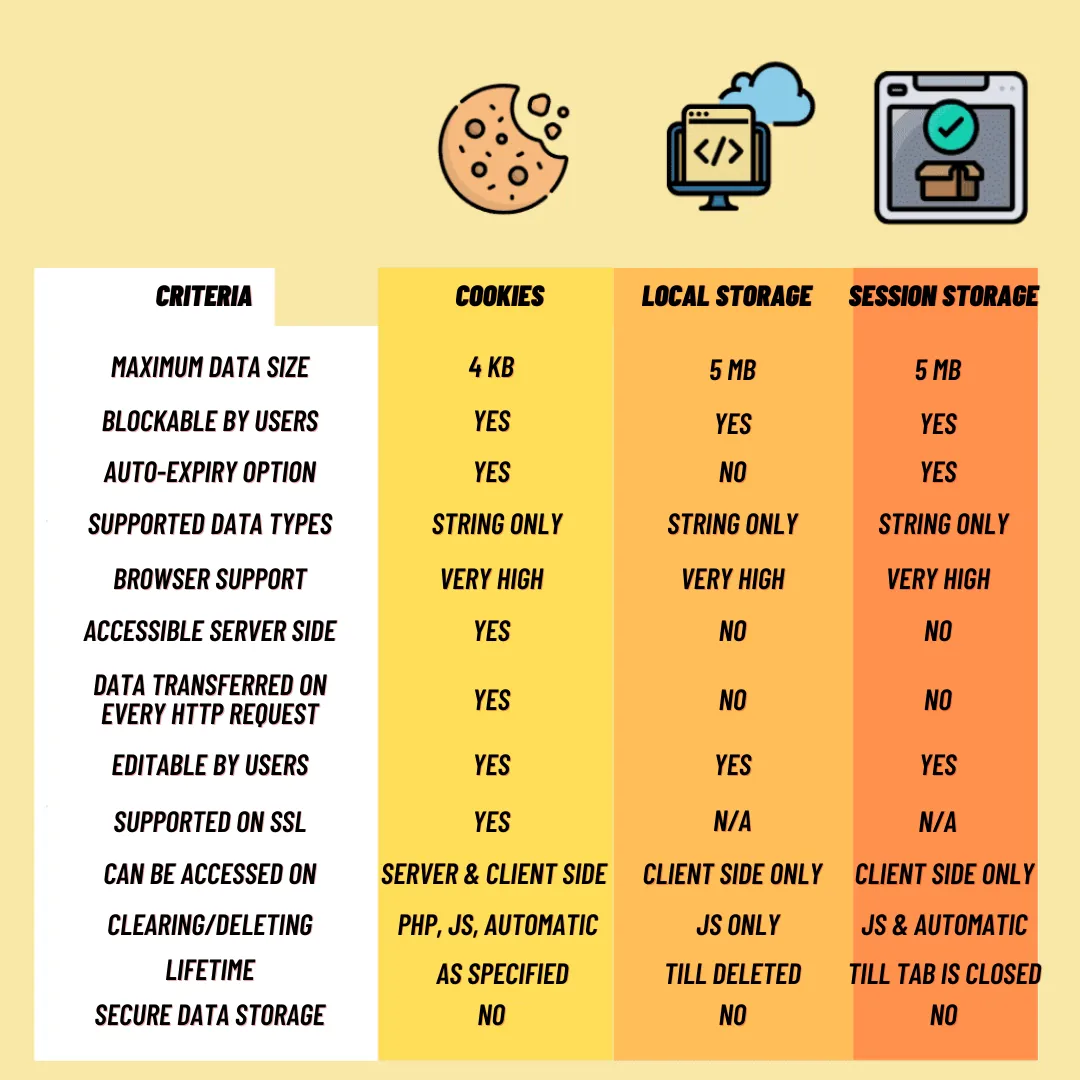
3. Comparison Table: A Quick Overview 📚
To make things clearer, here's a handy comparison table:
| Criteria | Cookie | LocalStorage | SessionStorage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capacity | ~ 4KB | ~ 5-10MB | ~ 5-10MB |
| Lifetime | Can be set | Persistent | Per session (tab) |
| Sent to Server | Yes (Automatic) | No | No |
| Access Scope | All windows/tabs | All windows/tabs (same origin) | One tab only |
| API | Complex, string-based | Simple, intuitive | Simple, intuitive |
| Created by | Client & Server | Client only | Client only |
4. Security Issues ⚠️
A very important point: All three storage mechanisms are not absolutely secure and can be vulnerable to Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks. Malicious JavaScript running on your site can read and steal all data in LocalStorage, SessionStorage, and Cookies (except Cookies with the HttpOnly flag).
Golden rule: NEVER store any sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, or important API tokens in any of these three mechanisms.
Conclusion: Choose the Right "Weapon" for the Right "Battle"
In the end, there is no absolute winner. The real "king" is the developer who knows how to choose the right tool for each specific task:
- Need a small "note" to communicate with the server and authenticate users? Use Cookies.
- Need a "durable locker" to store settings and app data across visits? LocalStorage is perfect.
- Need a "temporary memory" for data in a single process in one tab? SessionStorage won't let you down.
Understanding this trio not only helps you build better websites but also gives you the power to control your own data while browsing. Enjoy your journey exploring the world of web development!
![[JS Basics] Demystifying the this Keyword in JavaScript: When and How to Use It?](/images/blog/this-keyword-in-javascript.webp)
![[JS Basics] What is an Array in JavaScript? The Most Effective Ways to Use Arrays](/images/blog/arrays-in-javascript.webp)
![[JS Basics] Operators in JavaScript: Overview and Easy-to-Follow Practical Examples](/images/blog/basic-operators-in-javascript.webp)
![[JS Basics] JavaScript Events: A Guide to Effective and Optimal Event Handling](/images/blog/event-handling-in-javascript.webp)