If you’ve ever stepped into the world of React, you’ve probably heard the term Virtual DOM. It’s often described as "magic," a "secret weapon" that gives React its outstanding performance and a great developer experience.

But what exactly is the Virtual DOM? How does it work? And why is it so important? Let’s demystify this core concept in the most visual and easy-to-understand way.
The Backstory – Why is the "Real DOM" Slow?
Before understanding the Virtual DOM, we need to know its predecessor: the Real DOM.
DOM (Document Object Model) is a programming interface for HTML documents. Imagine it as a giant tree structure, where each HTML tag (like <div>, <p>, <span>) is a leaf (node). When you want to change anything on a web page—like changing a button’s color or adding a new comment—you have to manipulate this DOM tree directly.
The problem: Directly manipulating the Real DOM is expensive in terms of performance.
Every time a node in the DOM tree changes, the browser has to do a lot of heavy work:
- Re-calculate Styles: The browser recalculates CSS for the changed node and its children.
- Layout/Reflow: It recalculates the position and size of elements on the page. This is a complex process and can affect the whole page.
- Repaint: Finally, the browser "paints" the changed pixels on the screen.
Imagine you want to fix a sentence in a 1000-page book. Instead of just fixing that sentence, you rewrite the entire book. That’s the kind of waste that happens when you manipulate the Real DOM carelessly. As your app grows and changes state frequently, this leads to lag and a poor user experience.
This is where the Virtual DOM comes in.
What is the Virtual DOM? The "Architect" of the UI
Virtual DOM (VDOM) isn’t a browser feature or proprietary technology. At its core, it is:
A lightweight copy, a "blueprint" of the Real DOM, stored in memory as a JavaScript object.
Think of it this way:
- Real DOM is a real building. Changing it (knocking down a wall, adding a window) is costly and time-consuming.
- Virtual DOM is a detailed blueprint of that building. Editing the blueprint (erasing a wall, drawing a new door) is fast and cheap.
React uses this Virtual DOM blueprint to efficiently calculate what needs to change before touching the Real DOM.
The Magic Mechanism – Reconciliation & Diffing Algorithm ⚡️
This is the "magic" part of React. The process of efficiently updating the UI is called Reconciliation. The Virtual DOM is the main tool for this process.
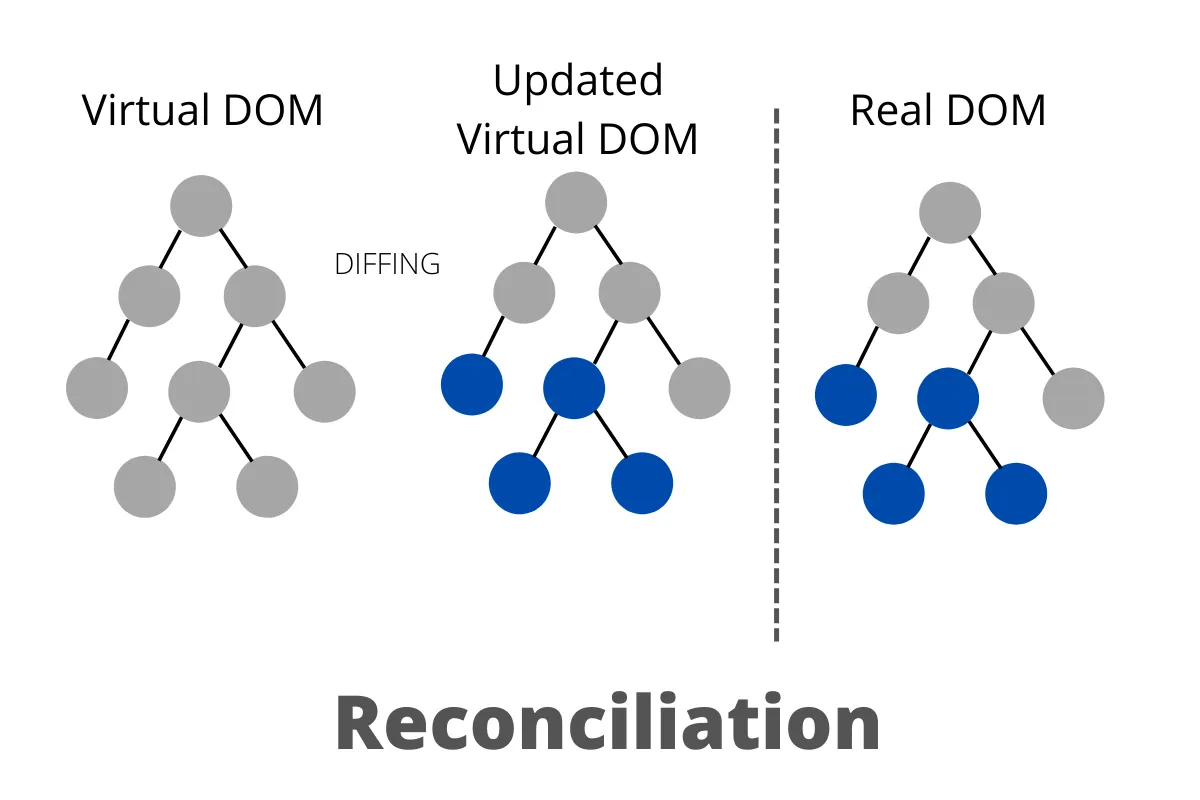
Here’s how the 4-step process works:
Step 1: State Changes
Everything starts when something changes in your app—like a user clicking a button, typing in an input, or receiving new data from the server. This changes a component’s state.
// Example: state changes on click
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
const handleClick = () => {
setCount(count + 1)
}
Step 2: Create a New Virtual DOM Tree
When state changes, React doesn’t rush to the Real DOM. Instead, it creates a new Virtual DOM tree from scratch. This is very fast because it’s just creating JavaScript objects in memory.
Step 3: Diffing Algorithm 🕵️♂️
Now, React has two blueprints:
- Old Virtual DOM: The snapshot of the VDOM before the state change.
- New Virtual DOM: The VDOM just created in Step 2.
React uses a smart Diffing Algorithm to compare these two trees and find the minimal set of differences. This algorithm is optimized based on a few assumptions:
- If two elements have different types (e.g.,
<div>to<span>), React destroys the old tree and builds a new one from scratch. - If two elements have the same type, React keeps the old DOM node and only updates changed attributes (like
className,style). - When handling lists, React uses the
keyprop to identify which items have changed, been added, or removed—without re-rendering the whole list. That’s whykeyis so important inmap()loops.
Step 4: Update the Real DOM (Commit)
After figuring out exactly what needs to change, React "batches" all these changes and updates the Real DOM in a single operation.
This is a "surgical strike." Instead of rebuilding the whole building, React sends a team to fix just the wall that needs changing. This minimizes expensive operations like Reflow and Repaint, resulting in great performance.
The Outstanding Benefits of the Virtual DOM
Using the Virtual DOM isn’t just a technical trick—it brings huge advantages:
-
High Performance: ⚡️ This is the most obvious benefit. By minimizing direct, expensive operations on the Real DOM, React apps are faster and smoother, especially with complex UIs and lots of changing data.
-
Better Developer Experience: 🛠️ Developers don’t have to worry about manual DOM management. You just declare what the UI should look like for each
state, and React (with the Virtual DOM) handles the rest. This makes code easier to read, maintain, and less error-prone. -
Platform Agnostic: 🌍 Because the Virtual DOM is just a JavaScript object, it’s not tied to the browser. This paved the way for React Native, letting developers use the same React model to build native mobile apps for iOS and Android.
Conclusion: Not Magic, But Smart Engineering
Virtual DOM isn’t some mystical technology—it’s a brilliantly engineered solution to a fundamental web development problem. It acts as an efficient middle layer, letting React update the UI in the most optimal way.
By understanding how the Virtual DOM works, you’ll not only become a better React developer, but also appreciate the elegance and power behind this amazing library. It’s proof that a smart abstraction can solve the hardest problems and reshape how we build the modern web.
Happy coding with React!
![[Advanced React] Virtualization in React: Optimizing Performance for Large Lists](/images/blog/virtualization-in-react.webp)
![[Advanced React] What is React Fiber? Understanding Its Architecture and How It Works](/images/blog/react-fiber.webp)
![[Advanced React] React Concurrent Mode: Taking App Performance to the Next Level](/images/blog/react-concurrent-mode.webp)
![[Advanced React] React Component Composition: Effective Advanced Techniques](/images/blog/advanced-react-component-composition.webp)