If you're starting your journey into the world of programming or looking to improve your workflow, you've probably heard the term Git Repository. But what exactly is it? Why is it considered the "heart" and "brain" of every modern software project?
Let's demystify this important concept in the most intuitive and easy-to-understand way. This article will help you go from "zero" to "hero" in mastering Git repositories.
Git Repository: More Than Just a Folder of Code 📂
Imagine you're writing a novel. You have your first draft, then you edit, add chapters, change the plot. It would be a disaster if you accidentally deleted a great section or wanted to revert to an old version but had no way to do so, right?
A Git Repository (often called a "repo") is like a magical "time machine" for your project.
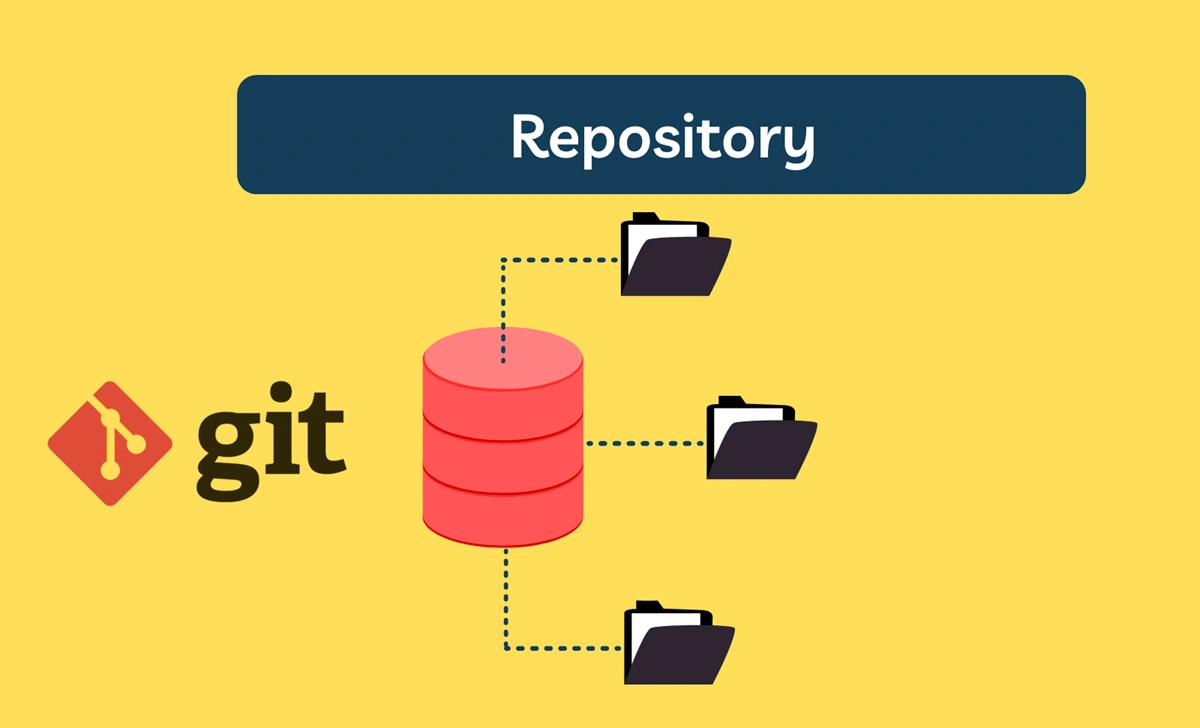
In essence, a Git Repository is a special folder that contains your project's entire source code, while also storing the complete history of every file change. Git doesn't just save the current state of your files; it takes a "snapshot" every time you make changes and records them.
This means you can:
- Revert to any previous version in the past.
- See who changed what, when, and why.
- Experiment with new features safely without worrying about breaking the original project.
The secret lies in a hidden subfolder called .git inside your project directory. This is the "black box" where all of Git's magic happens.
Types of Git Repository: Local and Remote - The Perfect Duo 🤝
In the world of Git, there are two main types of repositories that work together. Understanding the difference is key to working efficiently.
1. Local Repository
This is the repository on your own computer. It's a full copy of the project, including the entire change history. You can do everything—edit code, commit changes, review history, create branches—all completely offline.
- Speed: Since everything is on your machine, operations are extremely fast.
- Flexibility: You have full control and can work anywhere, even without Internet access.
2. Remote Repository
This is a repository stored on a remote server, usually on web platforms like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket. It acts as a collaboration hub and backup.
- Team collaboration: Everyone on the team can sync their work through the remote repository. This is the "single source of truth" for the whole team.
- Safe backup: If your computer fails, the entire project and its history are safely stored on the remote server.
- Access anywhere: You can access your code from any computer with Internet access.
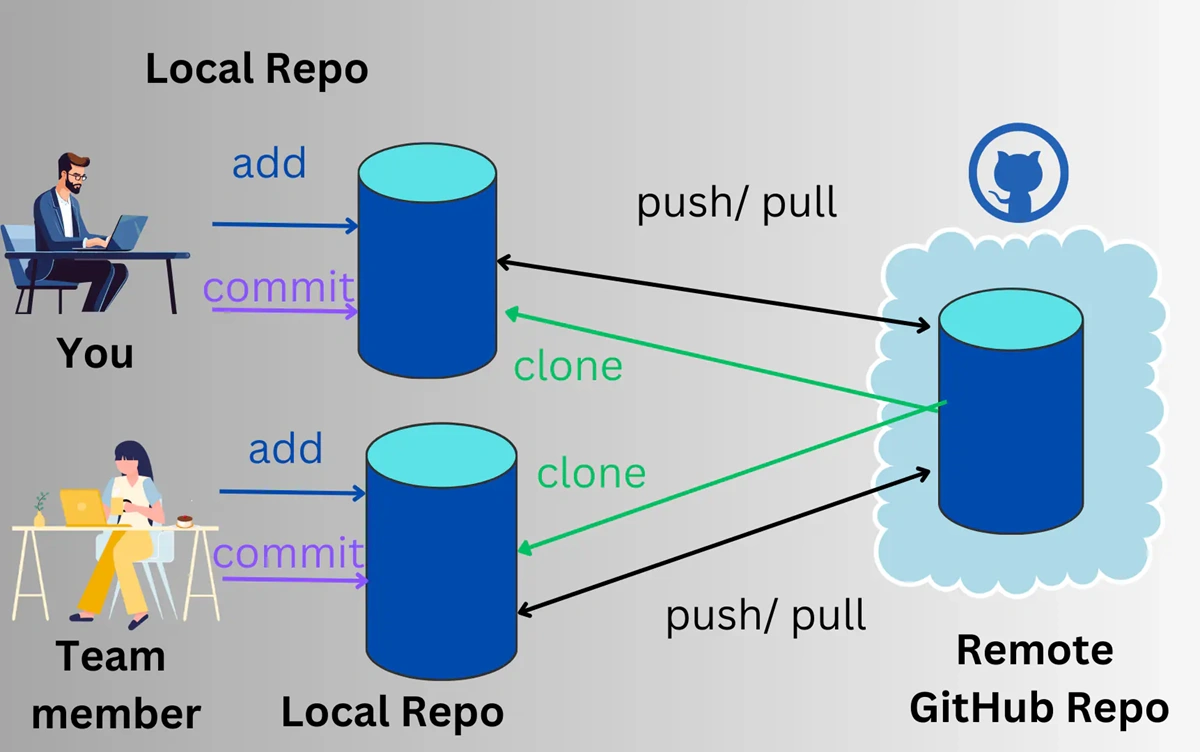
A common workflow: you pull the latest changes from the remote repo to your local repo, do your work, then push your changes back to the remote repo to share with everyone.
Why Is the Git Repository a Developer's Superpower? 🚀
Using a Git repository isn't just a good habit—it brings huge benefits that can transform how you develop software.
- Comprehensive version control: This is the core benefit. You have a clear history of your project's development, making it easy to track and debug.
- Frictionless collaboration: Git is designed for teamwork. Multiple people can work on the same project at once without stepping on each other's toes. Git's branching and merging system manages this complexity efficiently.
- Fearless experimentation: Want to try a wild new feature? Just create a new branch. A branch is an independent workspace. If your experiment succeeds, you can merge it into the main project. If it fails, just delete the branch. Your main project stays perfectly safe.
- Foundation of DevOps and CI/CD: Modern automation processes like Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are built around the Git repository. Every time code is pushed, build, test, and deployment processes can be triggered automatically.
Getting Started with Git Repository: Essential Commands 🛠️
Ready to create your first repository? Here are the most basic commands.
1. Initialize a New Repository (Local)
Open your terminal or command prompt, navigate to your project folder, and type:
git init
This command creates a hidden .git folder, turning your current directory into a Git repository.
2. Clone an Existing Repository (Remote)
To get a copy of an existing project from GitHub or another platform onto your computer:
git clone <REMOTE_REPOSITORY_URL>
This command creates a new folder containing the entire project and its history.
3. Basic Workflow
Once you have a repository, your daily workflow will revolve around these commands:
git add <file_name>: Stage your changes in the "staging area," preparing them to be recorded.git commit -m "Description of changes": Record the staged changes into the repository's history. The commit message is important so you and your teammates understand what changed.git push: Push your commits from the local repository to the remote repository.git pull: Update your local repository with the latest changes from the remote repository.
Conclusion: Git Repository Is the Essential Foundation
A Git repository is not just a tool—it's the foundation for collaboration, safety, and efficiency in modern software development. It's a detailed logbook, a safety net, and a shared meeting room for your entire development team. Mastering repositories will open new doors, helping you work more professionally and confidently.
Good luck on your journey to mastering Git!
![[Git Basics] Learn Git Branching: Essential Operations Everyone Should Know](/images/blog/basic-operations-with-git-branch-thumbnail.webp)
![[Git Basics] Mastering Git Merge with Detailed Guide and Examples](/images/blog/master-git-merge-thumbnail.webp)
![[Git Basics] Git Workflow: A Detailed Guide to Popular Team Collaboration Models](/images/blog/common-git-workflows-thumbnail.webp)
![[Git Basics] How to Effectively Resolve Merge Conflicts in Git](/images/blog/resolve-merge-conflicts-in-git-thumbnail.webp)