Imagine you are writing a novel. At first, you write alone, saving all drafts on your personal computer. But then, two friends join you as editors. How can all three of you work on a single file without stepping on each other's toes? How do you know who changed what, and when? And if your computer crashes, all your hard work could "vanish into thin air".
In the programming world, this problem is even more complex. And Remote Repository is the perfect solution.
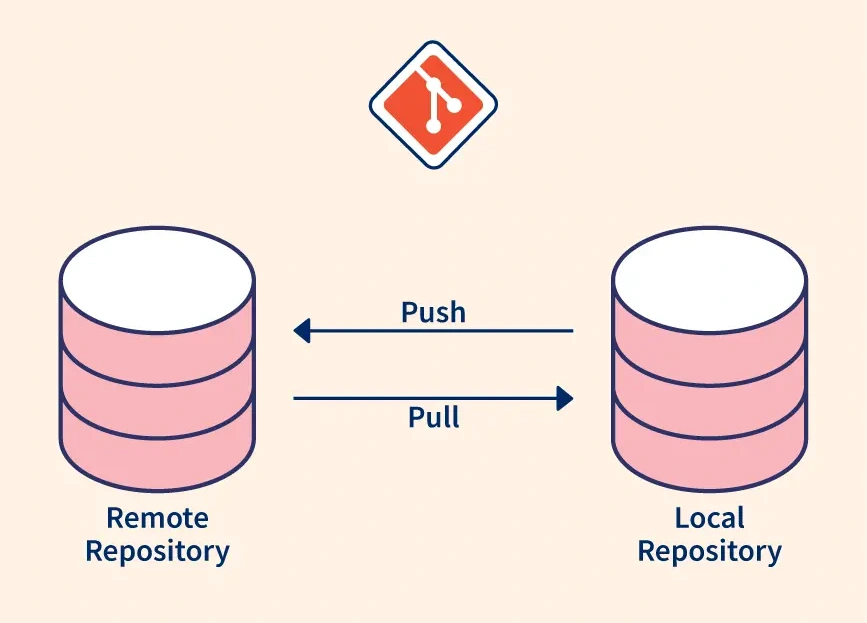
Simply put, a Remote Repository is a version of your project stored on the Internet or somewhere on a network. Think of it as a "shared home" 🏠, where all team members can safely share, synchronize, and store their source code.
If you work with Git, you have a Local Repository on your computer. This is where you do all your work: writing code, editing, committing changes. The remote repository is the central copy of that repository, hosted on a remote server.
Why is the Remote Repository so important?
Using a remote repository is not just a good habit—it's almost a requirement in professional software development. Here are the core reasons:
1. Foundation for "team collaboration" 🤝
This is the biggest benefit. A remote repository allows multiple developers from anywhere in the world to work on a project together. Everyone can pull the latest code, push their contributions, and easily review the project's entire change history. It eliminates the chaos of sending code back and forth via email or USB.
2. Safe and reliable backup ☁️
Your computer can be lost, your hard drive can fail, but your source code remains perfectly safe on the remote repository. This is the "cloud" backup for all your and your team's hard work. Losing code is one of the worst disasters for a developer, and the remote repository helps you sleep well at night.
3. Single Source of Truth 🎯
The remote repository acts as a coordination center, holding the "official" and most up-to-date version of the project. Everyone looks at a single source, ensuring all members work from the same foundation, avoiding unnecessary conflicts and misunderstandings.
4. Integration with CI/CD processes 🚀
In modern development, Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) are crucial.
Remote repository platforms often come with built-in tools for automatically testing, building, and deploying your application whenever a new change is pushed, helping to speed up and improve product quality.
How does a Remote Repository work?
The interaction between the local and remote repositories happens through a few basic but powerful Git commands:
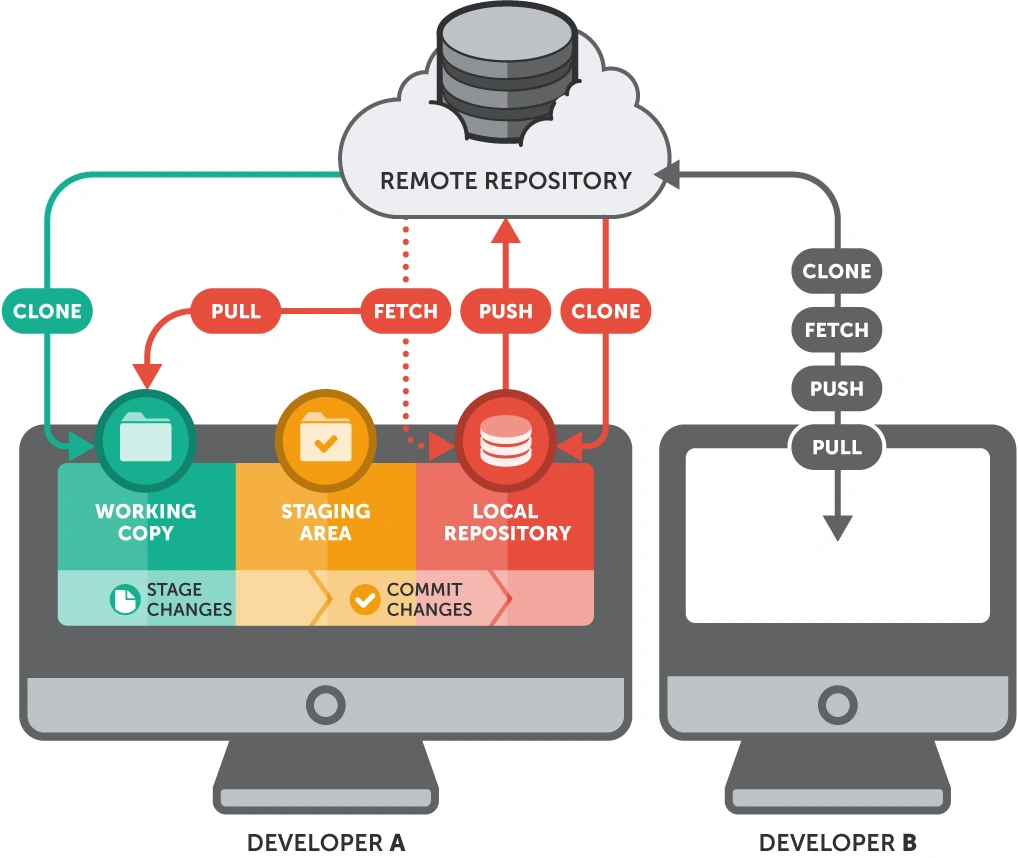
git clone: Use this command once when you first join a project. It creates a complete copy of the remote repository on your computer, including the entire change history.git push: After making and committing changes locally, usepushto send those changes to the remote repository, sharing them with everyone.git pull: When your teammates have pushed their changes, usepullto fetch those updates to your local repository, ensuring you always have the latest code. In fact,git pullcombines two commands:git fetch(get info about changes) andgit merge(merge those changes into your current branch).git fetch: This command downloads history and changes from the remote repository but does not automatically merge them into your working version. This lets you preview changes before deciding to integrate them.
The most popular Remote Repository platforms today
You don't need to set up your own server to store code. There are many great services providing this platform, each with its own strengths:

- GitHub: Known as the "social network for developers." It's the most popular platform, with a huge open-source community, friendly interface, and a powerful ecosystem (GitHub Actions, Copilot).
- GitLab: Famous as an "all-in-one" DevOps platform. GitLab not only provides code hosting but also has built-in CI/CD, project management, and security tools from the start.
- Bitbucket: Developed by Atlassian, Bitbucket integrates deeply and smoothly with their other products like Jira (task management) and Confluence (documentation), making it a top choice for businesses already using these tools.
There are also self-hosted options like Gitea, or you can use services from major cloud providers like AWS CodeCommit or Google Cloud Source Repositories.
Conclusion: Remote Repository is essential for teamwork
A Remote Repository is not just a place to store code. It can be seen as the nerve center, the heart of collaborative workflows in software development. It promotes transparency, ensures project safety, and opens the door to automation and efficiency. Mastering remote repositories is a foundational skill every professional developer must have.
![[Git Basics] How to Install and Configure Git Initially: What You Need to Know](/images/blog/how-to-install-and-configure-git-initially-thumbnail.webp)
![[Git Basics] What is a Git Branch? Mastering Branches in Git](/images/blog/what-is-git-branch-thumbnail.webp)
![[Git Basics] Understanding the File Life Cycle in Git: 3 States You Need to Know](/images/blog/file-life-cycle-in-git-thumbnail.webp)
![[Git Basics] What is the .gitignore File? How to Use It Effectively for Every Project](/images/blog/gitignore-file-thumbnail.webp)