When stepping into the React world, one of the first and most confusing technical questions is: "Is React Client-Side Rendering (CSR) or Server-Side Rendering (SSR)?". This is an extremely valid question, because the answer not only shapes how you build your application but also profoundly affects performance, SEO, and user experience.

The short and surprising answer is: React is inherently neither CSR nor SSR. React is a JavaScript library for building user interfaces (UI). It only cares about what will be displayed, based on state and props. As for where and when that interface is created (rendered) - on the user's browser (Client) or on the server (Server) - that's a different story.
Let's dissect each concept to understand the essence and explore the modern rendering world with React!
🏛️ Classic Foundation: React and Client-Side Rendering (CSR)
This is the most traditional and basic approach when you start with React, such as when using create-react-app or vite.
How does CSR work?
Imagine you're ordering a flat-pack furniture set. The delivery person (server) brings you a box containing:
- A very thin instruction sheet (nearly empty HTML file).
- Many pieces and screws carefully packaged (large JavaScript files, also called bundles).
Your task (browser - client) is to open the box, read the instructions, and assemble all the furniture by hand.
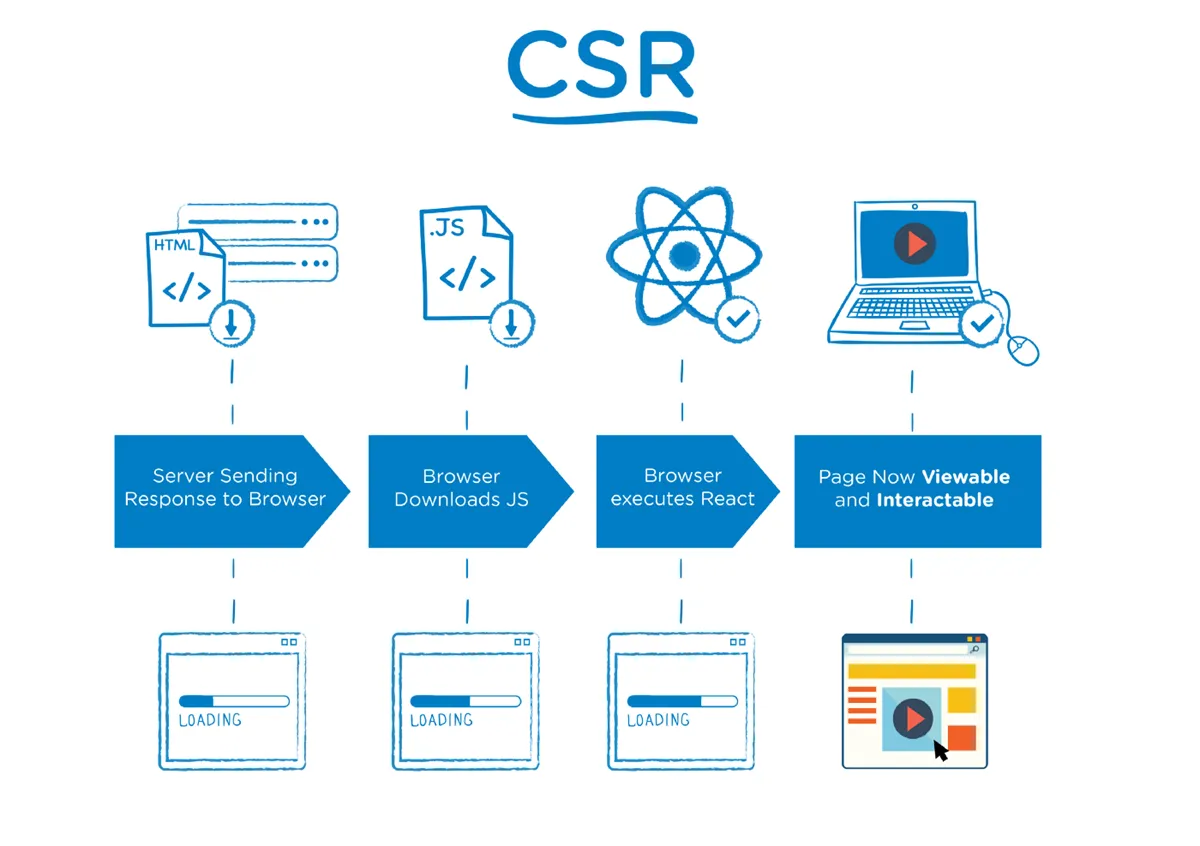
In the web world, this process happens as follows:
- The browser requests a web page.
- The server sends back a minimal HTML file, usually just a
<div id="root"></div>tag and a<script>tag pointing to React's JavaScript file. - The browser downloads that JavaScript file.
- React runs in the browser, "draws" the entire user interface inside the
<div id="root">, fetches data from APIs, and makes the web page interactive.
Advantages:
- Desktop app-like experience: After the first load, page transitions and interactions are very fast and smooth because you don't need to reload the entire page from the server.
- Reduces server load: The server only needs to send static files, all the heavy rendering work is handled by the user's machine.
Disadvantages:
- Slow initial load time: Users have to wait for the entire "chunk" of JavaScript to download before seeing content. This creates an annoying blank screen and poor metrics like Time to First Byte (TTFB) and First Contentful Paint (FCP).
- Poor SEO friendliness: Search engine crawlers when visiting might only see an empty HTML page, because they're not always patient enough to wait for JavaScript to finish running. Although Google has improved this, SEO remains a weakness of CSR.
When to use CSR? Very suitable for complex web applications, high interaction requirements, and don't prioritize SEO on the first page, e.g., admin dashboards, online editing tools, internal social networks.
🚀 Optimal Solution: React and Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
To fix the disadvantages of CSR, especially SEO issues and initial load speed, the community has turned to SSR. Frameworks like Next.js have become pioneers and the top choice for implementing SSR with React.
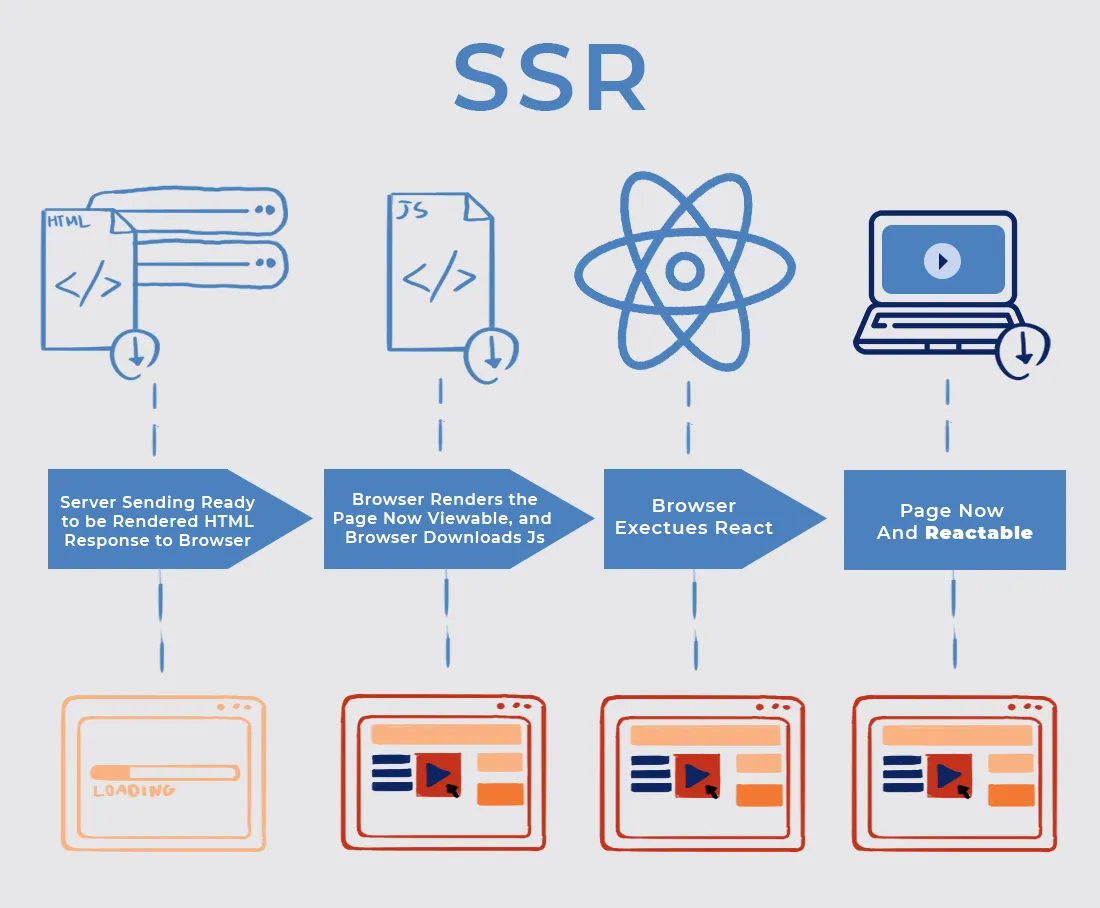
How does SSR work?
Back to the house example. Instead of buying flat-pack furniture, this time you order an item that's pre-assembled at the factory. The delivery person (server) brings you a complete product. You just need to place it in the room and use it immediately.
Technical process:
- The browser requests a web page.
- The server receives the request, runs React code on the server itself, fetches necessary data from the database or API.
- The server creates a content-complete HTML file and sends it to the browser.
- The browser immediately displays this HTML page to the user. Users see content very quickly.
- Meanwhile, the browser still downloads the JavaScript file. This process is called "Hydration" (watering), JavaScript will "come alive" on the static HTML page, attaching event handlers so the web page becomes interactive.
Advantages:
- Extremely fast initial load (Fast FCP): Users see content almost immediately, significantly improving user experience.
- Excellent for SEO: Search engines receive a complete HTML page, easy to index and rank.
- Better performance on weak devices: Reduces the burden of JavaScript processing for low-end mobile devices.
Disadvantages:
- Increased server load: The server now has to work harder for each request.
- Higher complexity: Setting up and managing an SSR environment is more complex than CSR.
- Time to Interactive (TTI) may still be slow: Although users see content early, they may not be able to interact immediately until the Hydration process is complete.
When to use SSR? Ideal for content-centric websites, requiring strong SEO and good user experience on first visit. Examples: news sites, blogs, e-commerce pages, product introduction pages.
🌌 New Era: Beyond CSR and SSR
The game doesn't stop there. The React ecosystem continuously evolves, bringing hybrid and superior rendering methods:
1. Static Site Generation (SSG)
- What is it? The entire website is rendered into static HTML files at build time, before any users visit.
- Representative frameworks: Next.js, Gatsby.
- Advantages: Fastest possible speed because it's just serving static files. Extremely secure and cost-effective for hosting.
- Ideal for: Blogs, documentation sites, introduction websites, portfolios – places where content changes little.
2. Incremental Static Regeneration (ISR)
- What is it? A genius combination of SSG and SSR. Pages are created statically at build time, but can be "regenerated" on the server side after a certain time interval (e.g., every 60 seconds) when users visit.
- Representative framework: Next.js.
- Advantages: You get the speed of static pages but content can still be updated without rebuilding the entire website.
- Ideal for: News sites, e-commerce pages with products that don't update too frequently.
3. React Server Components (RSC)
- What is it? This is the latest and most revolutionary evolution of React. RSC allows components to exist and render entirely on the server and doesn't send any JavaScript to the client.
- Advantages:
- Zero-Bundle Size: Static components (like header, footer, text) don't increase JavaScript file size.
- Direct backend access: Server Components can directly access the database or file system without creating API endpoints.
- Reduces client burden: Only components that need interaction (Client Components) send JavaScript to the browser.
- This is the future: RSC is reshaping how we think about React application architecture, allowing us to create faster and lighter applications than ever before.
Comprehensive Comparison Table: Rendering
| Criteria | Client-Side Rendering (CSR) | Server-Side Rendering (SSR) | Static Site Generation (SSG) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Load Speed | 🐢 Slow | 🚀 Fast | 🔥 Fastest |
| SEO | 😟 Poor | ✅ Good | ✅ Very Good |
| Server Load | Low | High | Very Low (only when building) |
| Complexity | Simple | Complex | Medium |
| Dynamic Data | Very Good | Good | Poor (needs hybrid solution) |
Conclusion: So what should you choose for your project?
Back to the initial question, React is neither CSR nor SSR. React is a flexible tool, and which rendering method you choose depends entirely on project requirements:
- Building an internal admin page, a complex tool? CSR is a simple and effective choice.
- Building a blog, e-commerce page, or any page that needs SEO and first-visit speed? SSR or SSG/ISR with Next.js is the path you should take.
- Building an introduction page, documentation, portfolio? SSG will give unbeatable performance.
Understanding the nature of each rendering method not only helps you confidently answer the question "Is React CSR or SSR?" but also equips you with knowledge to make correct architectural decisions, creating web products that are faster, more powerful, and more user-friendly for everyone.